
2004) and might be genetically linked with specific humoral responses ( Cotter, Ayoub & Parmentier 2005). Selection experiments with chickens suggest that changes in NAb levels parallel changes in primary antibody responses and general disease resistance (e.g. 1997 Carroll & Prodeus 1998 Boes 2000 Ochsenbein & Zinkernagel 2000). NAb serve a number of functions, including direct immediate control of novel bacterial and viral challenges, initiation of the complement enzyme cascade that results in cell lysis, regulation of self-reactive B and T cells, and clearance of damaged or transformed cells ( Reid et al. Unlike adaptive Ab, NAb are directly encoded by germ-line genes in the absence of somatic rearrangement ( Avrameas 1991 Boes 2000 Ochsenbein & Zinkernagel 2000) and, by definition, are the only class of immunoglobin molecules whose concentration in blood is not dependent on previous exposure to specific antigens ( Pereira et al. An important humoral component of constitutive, innate immunity are natural antibodies (NAb), which represent a first-line of defence against pathogens ( Ochsenbein & Zinkernagel 2000). Less attention has been paid to constitutive immune function in wild populations. changes in leukocyte profiles, often after a specific or non-specific challenge). antibody responses to specific antigens) and cellular immunity (e.g. Much recent work on immune function in developing birds has focused on measuring induced immunological responses, a subset of immune function that involves adaptive humoral immunity (e.g. Merino, Moller & de Lope 2000 Dubiec & Cichon 2001 Hoi-Leitner et al. Response to PHA is typically positively correlated with nestling body condition or food availability, sometimes mediated through an effect of brood size or season (e.g.
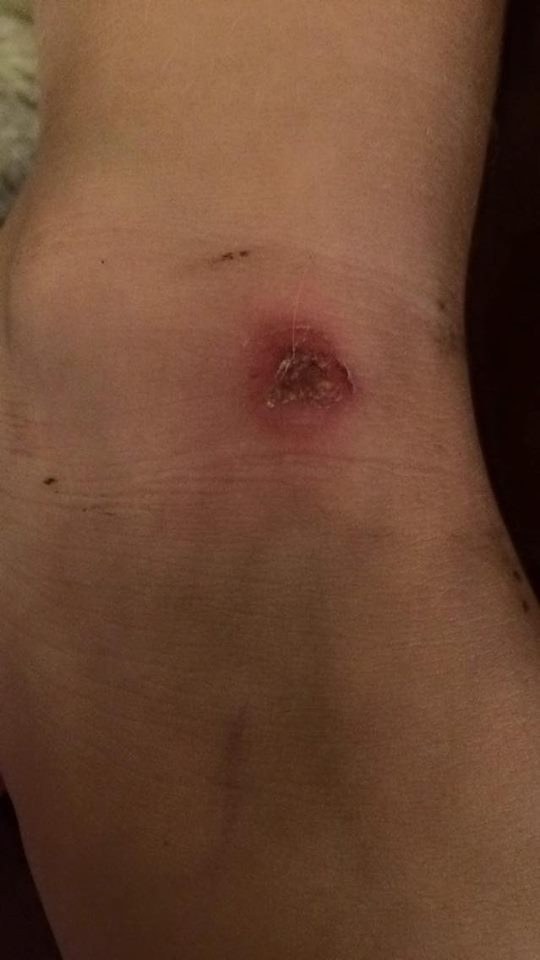
Although the PHA response involves proliferation of T cells, PHA also attracts other immune cells, including basophils and heterophils, to the injection site and causes inflammation ( Smits, Bortolotti & Tella 1999).
#Maxbulk mailer infection skin
2002) have employed the phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) skin test to assess non-specific cellular immunity (commonly referred to as cell-mediated immunity, or CMI).

2004) and increase metabolic rate ( Ots et al. 2003 Brommer 2004a), degrade adult body condition ( Alonso-Alvarez & Tella 2001 Sanz et al. For example, experimentally elicited immune responses have been shown to decrease avian nestling growth ( Fair, Hansen & Ricklefs 1999 Alonso-Alvarez & Tella 2001 Whitaker & Fair 2002 Nilsson 2003 Soler et al. With benefits come costs resources allocated to the immune system are not available for other functions. 2001 Svensson, Sinervo & Comendant 2001 Råberg & Stjernman 2003). 2000 Alonso-Alvarez & Tella 2001 Christe et al.

The ability to respond effectively to parasites and pathogens has been shown to have fitness benefits in terms of body condition, survival and reproductive success (e.g. 2001 Tella, Scheuerlein & Ricklefs 2002 Schmid-Hempel 2003). Immune function is increasingly seen in the context of life-history trade-offs ( Sheldon & Verhulst 1996 Norris & Evans 2000 Martin et al. While such a relationship is consistent with the idea that immune function development involves trade-offs, the processes involved are more complex than simple energy allocation. This suggests that individuals with low initial NAb levels accelerate immune development to reach adult levels, whereas individuals with high initial levels do not.Īs in previous studies, our results demonstrate an inverse relationship between growth rate and development of components of the avian immune system. Initial titre levels were inversely proportional to rate of change in NAb levels over the first 50 days of immune development. NAb levels increased over the first 50 days of chick development however, rate of increase was inversely proportional to wing growth. We used natural variation in nestling growth to assess the influence of nutritional status on the development of innate immunity. We measured levels of natural antibodies (NAb) during the early, middle and late phases of storm-petrel development and related these levels and NAb rate of change to mass and wing length growth. Using a simple technique for assessing constitutive innate immune function recently adapted for use in wild populations, we characterize changes in avian immune system development by repeated measurements of individuals over the period of nestling growth in a wild population of Leach's Storm-Petrels ( Oceanodroma leucorhoa).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
